what powers of congress are unique to the senate
Powers
Delegated powers require both houses of Congress to work with each other. These powers are the powers to:
-
to tax
-
borrow money
-
regulate commerce
-
enhance an army
-
create and make rules for federal courts
-
plant naturalization laws
-
plant postal service offices
-
provide a militia
-
make laws necessary and proper to carry out 👆these powers
Congress also has the ability of the purse which gives the Congress to influence the president or bureaucracy by withholding or putting conditions on funding. The power of the purse tin exist used to promote specific programs or lessen the ability of an agency and the power of the purse has been used past Congress to limit executive power.
Powers Unique to One Sleeping accommodation
The Firm of Representatives can but initiate taxation laws and spending bills. Thus, the Business firm Ways and Ways Committee oversees taxing and spending legislation. The Senate can only amend revenue bills.
Some of the Senate'due south unique powers include confirming president nominations to federal courts or ambassadorships to foreign countries, confirming members of the president'southward cabinet, and ratifying treaties signed by the president.
Congressional actions do take restrictions meaning that Congress can't laissez passer bills of attainder or ex post facto laws, levy export taxes, or grant titles of nobility.
Congressional Oversight and Transparency
Congress performs oversight through committees and subcommittees to review the work of executive agencies which provides a check on the executive branch. Congress investigates corruption and waste and also calls on experts and citizens to testify at hearings to discuss the authorities'due south problems and provide solutions. All of the committee chairs have the power to legally compel witnesses to appear and testify.
Committee hearings and flooring fence help to increment the public's knowledge of the government and societal issues. Floor debates can garner national attention considering of issues like gun control, revenue enhancement cuts, Social Security reform, healthcare reform, and sending armed troops abroad.
Legislative Procedure
The legislative process is dull by design which prevents Congress from acting hastily. The framers intended that this would allow for compromises to be met, but in reality concluding versions of bills are vastly different from the initial versions.
Bills can be written by members of Congress and their staff or the executive branch and are introduced by a fellow member of Congress. They tin can also be suggested and written by interest groups and their attorneys.
Information technology doesn't matter who authors a bill, just just a fellow member of Congress tin can innovate it and the member who introduces the nib becomes its sponsor.
The legislative process allows for both the House and Senate to work with each other and the bills must exist in exactly the same class when they pass both houses. The debating and voting processes in both Chambers differ because of the size of their memberships.
Structure
Rules in the House of Representatives
Since the Firm of Representatives has 435 members the process of debating bills is limited. The Senate only has 100 members, and so there are relatively few rules governing information technology.
The Firm Rules Committee is responsible for determining how long a nib volition be debated and, whether to allow open or closed rules for amending bills. An open rule allows amendments to be added to bills, but airtight rules prevent amendments from being added to bills.
The Firm Rules Commission has been considered i of the most powerful committees in the house because information technology controls crucial aspects of the legislative process. The Rules Committee can kill a neb by delaying a vote, allow information technology to exist easier for opponents to add toxicant-pill amendments, or bring the bill up for an immediate floor vote.
Time allotted for debating the bill in question is dissever equally betwixt its proponents and opponents. The commission cannot itself pass legislation but may debate and suggest amendments.
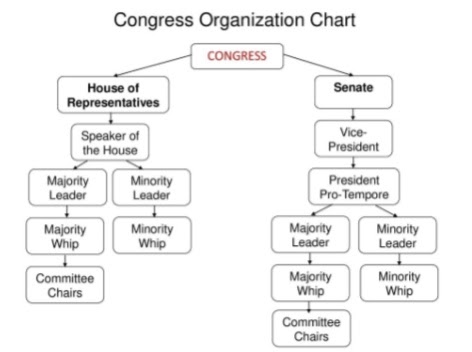
Important Roles in the House
The Speaker of the Business firm is the constitutionally mandated presiding officer of the Business firm of Representatives. The Speaker is chosen in the caucus of the majority party and is empowered to:
-
recognize members to speak on the flooring
-
dominion whether a move is germane
-
assign bills to committee
-
engage House members to select and joint committees
-
appoint the majority members of the Rules Committee.
Hither are some more key figures:
-
Firm Bulk Leader: has control of the dominant party in the lower house
-
is responsible for enactment of their political party's programs
-
-
House Majority Whip majority: a party leader in the lower house
-
exerts force per unit area on political party members to vote with the political party
-
responsible for getting their party's program enacted into law
-
-
The House Minority Leader: leader of the minority party in the lower house
-
responsible for informing party members and organizing resistance to programs submitted by the majority
-
Of import Roles in the Senate
-
President of the Senate: Vice President of the US
-
constitutional duty is to oversee the processes of the Senate
-
tin only vote if in that location is a tie
-
-
President Pro Tempore: most senior fellow member of the majority party and has been appointed to make full in for the Vice President as presiding officer
-
typically a ceremonial role
-
junior members of the majority party are rotated and appointed equally presiding officer to give them parliamentary procedure practise
-
-
Senate Bulk Leader: office of leadership in the upper business firm
-
responsible for passage of the majority party'southward programs
-
informs and pressures political party members to vote for programs
-
determine the gild in which bills are to exist debated
-
assign members to committees.
-
-
Senate Majority Whip: banana majority leader of the upper house He or she
-
assists the floor leader
-
communicates party positions
-
rallies the party members for crucial votes
-
orchestrates party back up for of import legislation
-
-
Senate Minority Leader: leader of the minority political party in the upper house
-
responsible for resisting programs submitted by the majority party
-
-
Senate Minority Whip: assistant minority political party leader in the upper business firm
-
reminds members about party positions
-
informs them when important bills are scheduled for a vote
-
orchestrates party opposition to majority bills
-
-
Committee Chairperson: committee heads
-
decides which bills to hash out and may kill a beak
-
selected by the Majority Leaders in both houses
-
Rules in the Senate
A debate in the Senate does not have a fourth dimension limit, so senators tin can contend for equally long as they want.
A delay is a tactic used to filibuster a vote on a bill and tie up the work of the Senate, because a senator makes a speech that continues for hours on the Senate floor. The only way to terminate a filibuster is to vote for a cloture. A cloture requires votes from 60 members to finish the filibuster.
Earmarks are provisions within legislation that appropriate money to a specific project in appropriations and authorization bills. Logrolling is when two legislators agree to trade votes for each other's benefit.
Pork butt legislation is the use of federal funding to finance localized projects, typically bringing money into a representative's district in order to please constituents and boost the representative'southward chances of winning reelection.
Afterward debates, the bills usually laissez passer in the House and Senate in different forms, and so both versions are sent to a conference committee. The conference commission came from the committees in the house and Senate that wrote the beak.
Functions
Most of the legislative business in Congress is done in committees. The bulk political party in ability holds all the committee chairs and majority of seats on the committees allowing the party in ability to control all the business of the committees.
Committees
Almost of the legislative work is done in committees, and almost proposed bills die in commission.
The Standing Committee is a legislative panel with total legislative functions and oversight responsibilities. The members get experts in their respective topic and examples of committees include the Appropriations Committee (sets specific expenditure for the federal regime) and the Armed Services Commission (oversees military and defense).
A sub-committee is formed to investigate specific topics within a standing committee. Examples include the Livestock, Dairy, and Poultry (sub committee of agriculture) and the Health Care Subcommittee (sub committee of finance committee).
Select Committees are temporary committees with limited purposes in areas like investigation.
A Joint Committee involves members of both the House and Senate, and they have jurisdiction over matters of joint interest. An example of a joint committee is the Joint Committee on the Library, only near joint committees are permanent (as with the Library Committee) but temporary articulation committees have been created to accost specific issues (such as the Articulation Committee on the Conduct of the War during the American Civil War).
The conference commission tries to negotiate a compromise beak that is acceptable to both the House and Senate. When a compromise version of the bill has been written, the neb goes to both houses for a vote, and if passed in both houses, it goes to the White Business firm for the president to sign it.
The President's Desk
When the president gets a bill, he must decide whether to sign or veto legislation within x days (excluding Sundays) while Congress is in session. At that place are three things the president can practice. If the president signs the bill, information technology becomes police force. He tin can as well veto the bill. The last selection is that the president tin 'sit' on the bill and take no action. Later on ten days (excluding Sundays), the bill becomes law without the president'south signature.
If a president takes no activity and sits on the beak and Congress adjourned before the ten-twenty-four hour period menstruation ended, the bill becomes pocket vetoed. When a bill is pocket vetoed it must go through the entire legislative process once more.
When the president vetoes a neb, Congress has 2 options: either make the suggested changes to the neb or try to override the veto by a ii-thirds vote. If the bill receives a two-thirds vote in both houses, it becomes police force without the president's signature or if the house the nib originated in does nothing, the beak is expressionless.
Resources:
fewingsthavatabot.blogspot.com
Source: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-gov/unit-2/structures-powers-functions-of-congress/study-guide/zHM0wXD3wtKBOJe1wrvE